What Is STEM Education and Why It Matters Today
Have you ever heard someone talk about a career in STEM? If not, STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics — and it’s becoming one of the most important areas in modern education. Imagine STEM as playing multiple sports at once — you can’t just choose one you like.
That’s because STEM education integrates all four disciplines into a single learning program that reflects how problems are solved in the real world.
STEM touches every aspect of our lives:
- Science helps us understand the world around us.
- Technology is embedded in almost everything we do.
- Engineering transforms our environment.
- Mathematics underpins nearly every profession.
A STEM curriculum introduces students to real-life situations and challenges, sparking interest in careers that shape the future. To benefit fully from the program, students are encouraged to embrace the interconnectedness of all four fields — not just focus on their favorite.
Rather than teaching science, math, technology, and engineering as separate subjects, STEM merges them into a real-world applicable framework. As we explore deeper in this article, you’ll gain a clearer understanding of the purpose of STEM and the value it offers to students and society.
What You Should Know About STEM
Although STEM emphasizes all four areas, science and mathematics are generally the foundation. The key difference is that while engineering and technology often involve building and creating, science and math tend to focus more on problem-solving — which some students find less exciting.
That said, mastering all four subjects is central to STEM. And even if you’ve struggled with these areas before, that doesn’t mean STEM is off-limits — it just means your journey may require more effort. Fortunately, the hands-on, practical nature of STEM often makes learning more accessible.
Here are several essential things to know about STEM’s approach and benefits:
1. A New Learning Style
Combining multiple courses into a single discipline breaks away from traditional classroom models. STEM brings together students from diverse academic backgrounds to tackle shared challenges.
Instead of giving direct instructions, educators in STEM encourage creative and flexible thinking. Students are expected to analyze problems independently and test possible solutions. Over time, teachers guide and support them — but the initiative begins with the student.
This independent thinking — rather than rote memorization — is at the heart of the new STEM mindset.
2. STEM Involves a Heavy Workload
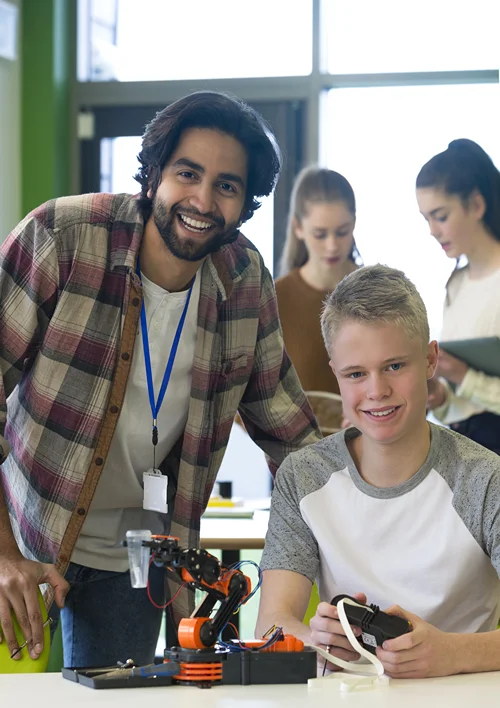
Compared to other learning systems, the workload in STEM programs, for example, in English school Limassol – Trinity, is notably heavier. With four disciplines combined, students must handle complex assignments and longer hours.
STEM learners are often viewed as creative and gifted, so the curriculum pushes them harder — preparing them for real-world demands. One mistake might mean starting from scratch, especially in fields like software development, where a single error can have major consequences.
That’s why the workload isn’t just academic — it’s mental training for high-stakes environments.
3. STEM Encourages Active Learning
No one goes through a STEM program just to passively earn a degree. Why study robotics if you’re not building robots that follow your commands?
Active learning means getting involved, experimenting, and applying your skills. STEM requires discipline and hands-on practice. The process builds not only technical abilities but also confidence and creativity.

The Benefits of STEM Education
Having looked at the structure and purpose of STEM, let’s dive into the specific benefits students can gain from participating in a STEM program starting from middle school.
-
Critical Thinking
STEM students become skilled at analyzing problems, thinking critically, and finding solutions — skills that apply both in and out of the classroom.
-
Innovation
STEM projects challenge students to try new things and think outside the box. This habit of innovation prepares them to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.
-
Project Management
By working on complex, team-based assignments, students develop leadership, communication, and time-management skills essential for career success.
-
Teamwork
Students learn to collaborate, understand each other’s strengths and weaknesses, and appreciate diverse ways of thinking — all while working toward a shared goal.
-
Confidence
Completing challenging projects boosts a student’s self-esteem and belief in their ideas. This sense of achievement can have lasting effects in their careers and lives.
-
Creativity
STEM isn’t about memorizing facts. It’s about imagination, experimentation, and building new ideas. Creative thinking is a core skill fostered by the STEM approach.
-
Real-World Problem Solving
STEM students develop strategic ways to solve real-world problems, test ideas, and learn from failure. The experience builds resilience and perseverance.
-
Scientific Literacy
From digital tools to scientific research, STEM teaches students how to critically analyze information and make informed decisions — an essential skill in today’s media-saturated world.
-
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Through group work and collaboration, students grow emotionally — developing empathy, patience, and the ability to work with others. Emotional intelligence is a key part of the STEM experience.
-
Adapting to a Changing World
In a world where technology and global challenges are constantly evolving, STEM gives students the skills they need to adapt and lead in uncertain environments.
Final Thoughts
STEM education is more than a curriculum — it’s a launchpad into the future. Yes, it’s demanding. Yes, it requires time and dedication. But for students who stay focused and curious, the rewards are extraordinary.
Whether your child is in kindergarten or already choosing a major, it’s never too early — or too late — to start the STEM journey.