Celebrating Academic Journeys with Meaningful Graduation Traditions
Graduation marks a pivotal milestone in every student’s life. It’s more than just a ceremony—it’s a celebration of hard work, commitment, and growth. As students prepare to walk across the stage, many look for meaningful ways to reflect their personal journey and achievements.
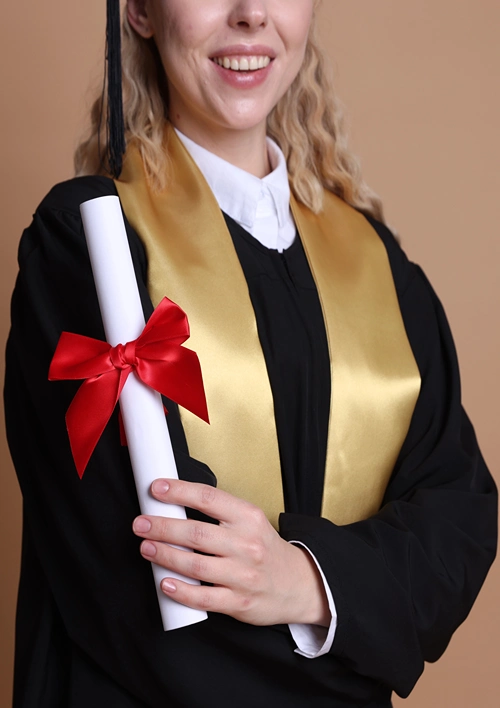
While caps and gowns have long been part of the tradition, one accessory is steadily gaining popularity and significance: the education graduation stole. This often-colorful sash worn over the graduation gown has evolved into a symbol of identity, pride, and personal story.
Whether it highlights cultural roots, academic honors, or club affiliations, the stole is an increasingly cherished part of graduation for students across the world.
The Rise of the Graduation Stole as a Symbol of Inclusion
In recent years, students have started using stoles to represent their unique journeys. From first-generation college graduates to students representing LGBTQ+ communities, stoles have become a platform for self-expression and acknowledgment.
This is especially important in today’s educational climate where inclusivity and diversity are not just celebrated—they’re essential. A graduation stole isn’t just an accessory anymore; it’s a symbol of resilience, achievement, and representation.
For students of color or those from marginalized communities, the stole can signify a journey that includes overcoming societal and institutional barriers. It’s a visible badge of honor that says, “I made it—and here’s who I am.”
Personalization: More Than Just a Trend
Gone are the days when stoles were generic. Students now seek stoles that are customized to reflect their academic paths, heritage, extracurricular passions, and future goals. A future engineer might choose a stole embroidered with a gear icon and their graduation year. A valedictorian could have gold trim and honors insignia.
This move toward personalization isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about storytelling. When families and friends see a graduate walk across the stage wearing a custom stole, they witness more than a moment—they see a narrative. One that includes late-night study sessions, student leadership, community service, and so much more.
Websites like mygradstoles.com have made it easier than ever to design high-quality, custom graduation stoles that allow students to reflect their individuality. Whether you’re looking to highlight your academic achievements or your cultural heritage, customization offers a powerful way to make your mark.
Encouraging Safe and Positive Digital Celebrations
As online sharing becomes part of the graduation experience, digital safety should not be overlooked. Many students proudly post graduation photos on social media—often wearing their stoles and sharing personal milestones. Young graduates must understand the importance of privacy settings, secure sharing, and being mindful of what they post online.
Parents and educators can play a role in helping students navigate the digital side of graduation. Encourage thoughtful sharing, and consider celebrating with private online gatherings or moderated photo-sharing platforms. This ensures a safe space for joy and recognition, free from the risks that can come with public online exposure.
Safe Search Kids has long been an advocate for educating parents, teachers, children and teens about smart digital choices. Graduation season is a great opportunity to reinforce those lessons in real-world situations, combining personal celebration with responsible tech use.
Bringing It Full Circle
Ultimately, the education graduation stole is more than a fashion trend—it’s a modern tradition rooted in meaning. Whether you’re a high school senior preparing for the next big leap or a college student closing one chapter to begin another, your stole is a banner of your story.
As families, teachers, and communities gather to cheer for the next generation of thinkers and doers, it’s essential to celebrate the whole person—what they’ve achieved, what they represent, and where they’re headed.
So when graduates step across that stage with a custom stole draped proudly over their shoulders, they’re not just marking the end of their education journey. They’re showcasing the full spectrum of their identity, one thread at a time.
Final Thoughts
Graduation is an emotional, transformative experience. The growth it represents deserves more than a fleeting moment; it deserves meaningful symbols that last. With the help of platforms like mygradstoles.com, students can make their education graduation stole a piece of history, memory, and pride.
Let’s continue to encourage our students to celebrate who they are—boldly, safely, and with joy.





 Katie Brenneman is a passionate writer specializing in education, mental health, family lifestyle and online safety. When she isn’t writing, you can find her with her nose buried in a book or hiking with her dog, Charlie. You can follow her on
Katie Brenneman is a passionate writer specializing in education, mental health, family lifestyle and online safety. When she isn’t writing, you can find her with her nose buried in a book or hiking with her dog, Charlie. You can follow her on